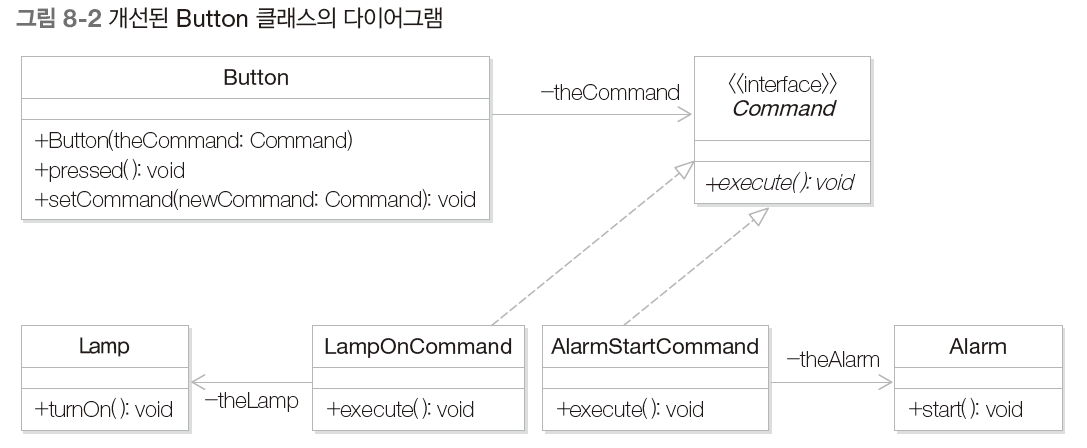
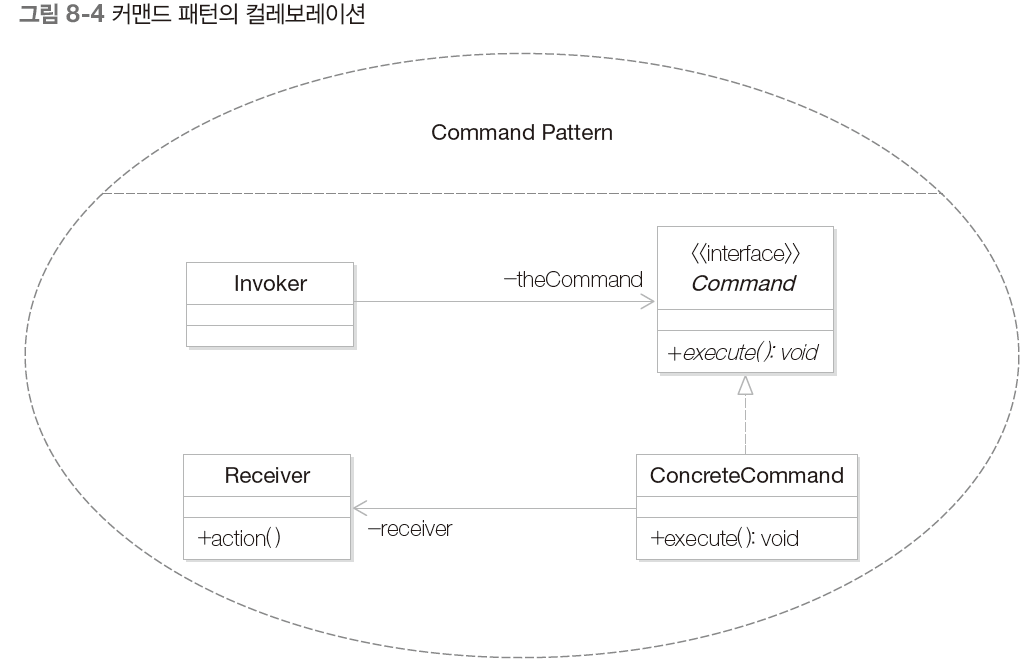
커맨드 패턴은 이벤트가 발생했을 때 실행될 기능이 다양하면서도 변경이 필요한 경우에 이벤트를 발생 시키는 클래스를 변경하지 않고 재사용하고자 할때 사용하는 패턴
🚴🏼 눌리면 특정 기능을 수행하는 버튼의 예를 들어보자
버튼을 눌렀을 때 램프의 불이 켜지는 프로그램을 개발하려면 버튼이 눌러졌음을 인식하는 Button 클래스, 불을 켜는 기능을 제공하는 Lamp 클래스가 필요하다. 그리고 버튼을 눌렀을 때 램프를 켜려면 Button 클래스는 Lamp 객체를 참조해야 한다.
Lamp
1
2
3
4
5
public class Lamp {
public void turnOn() {
System.out.println("Lamp On") ;
}
}
Button
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Button {
private Lamp theLamp ;
public Button(Lamp theLamp) {
this.theLamp = theLamp ;
}
public void pressed() {
theLamp.turnOn() ;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lamp lamp = new Lamp() ;
Button lampButton = new Button(lamp) ;
lampButton.pressed() ;
}
}
But,
버튼을 눌렀을 때 다른 기능을 실행할 경우와, 버튼을 누르는 동작에 따라 다른 기능을 실해하는 경우 모두 Button 클래스를 수정해야 된다. 즉, 다른 기능(알람 동작)을 추가하거나 변경할 때 메서드를 변경해야 하므로 OCP를 위배하게 된다.
**해결책
- 버튼은 수행될 기능을 캡슐화된 객체로서 전달 받음
- 버튼이 눌리면 전달 받은 객체를 호출함으로써 구체적 기능을 수행
Command interface
1
2
3
public interface Command {
abstract public void execute();
}
1
2
3
public class Lamp {
public void turnOn() { System.out.println("Lamp On") ; }
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class LampOnCommand implements Command { // 램프를 켜는 기능의 캡슐화
private Lamp theLamp;
public LampOnCommand(Lamp theLamp) {
this.theLamp = theLamp ;
}
public void execute() { theLamp.turnOn() ; }
}
1
2
3
public class Alarm {
public void start() { System.out.println("Alarming...") ; }
}
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class AlarmOnCommand implements Command { // 알람을 울리는 기능의 캡슐화
private Alarm theAlarm ;
public AlarmOnCommand(Alarm theAlarm) {
this.theAlarm = theAlarm ;
}
public void execute() { theAlarm.start() ; }
}
Button
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Button {
private Command theCommand ;
public Button(Command theCommand) {
setCommand(theCommand) ;
}
public void setCommand(Command newCommand) {
this.theCommand = newCommand ;
}
// 버튼이 눌리면 주어진 Command의 execute 메서드를 호출함
public void pressed() {
theCommand.execute() ;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lamp lamp = new Lamp() ;
Command lampOnCommand = new LampOnCommand(lamp);
Button button1 = new Button(lampOnCommand) ; // 램프를 켜는 기능을 설정함
button1.pressed() ;
Alarm alarm = new Alarm() ;
Command alarmOnCommand = new AlarmOnCommand(alarm) ; // 알람을 울리는 기능을 설정함
Button button2 = new Button(alarmOnCommand) ;
button2.pressed() ;
button2.setCommand(lampOnCommand) ; // 알람을 울리는 기능을 설정함
button2.pressed() ;
}
}
버튼이 눌렀을 때 필요한 임의의 기능은 Command 인터페이스를 구현한 클래스의 객체를 Button 객체에 설정해서 실핼할 수 있다. 따라서 Button 클래스는 소스코드를 변경하지 않으면서도 다양한 동작을 구현할 수 있다.
커맨드 패턴은 실행될 기능을 캡슐화함으로써 기능의 실행을 요구하는 호출자(Invoker) 클래스와 실제 기능을 실행하는 수신자(Recevier) 클래스 사이의 의존성을 제거한다. 따라서 실행될 기능의 변경에도 호출자 클래스를 수정 없이 그대로 사용할 수 있도록 해준다.
- Button 클래스는 Invoker 역할을 한다.
- LampOnCommand와 AlarmOnCommand는 ConcreteCommand 역할을 한다.
- Lamp 클래스와 Alarm 클래스는 Receiver 역할을 한다.