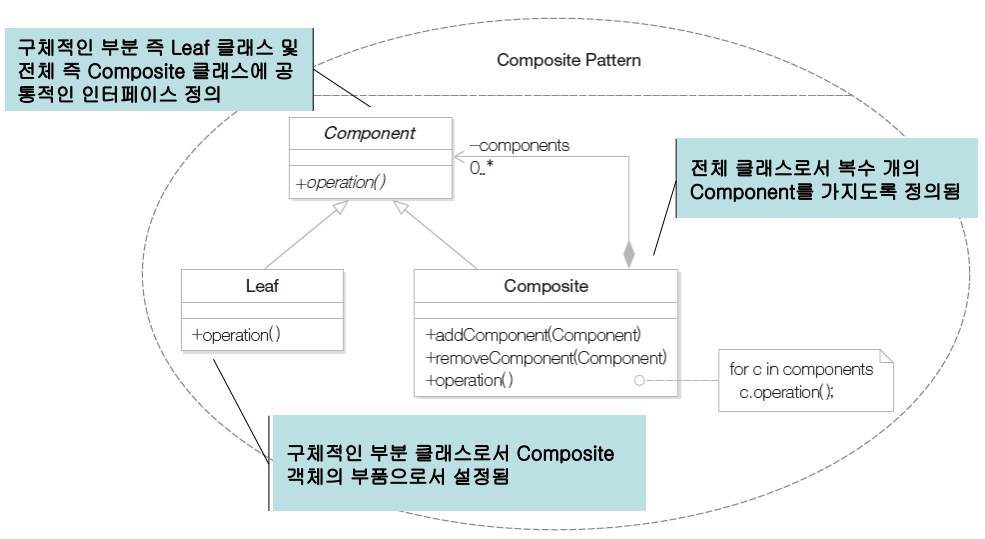
부분과 전체의 계층을 표현하기 위해 객체들을 모아 트리 구조로 구성한다. 사용자로 하여금 개별 객체와 복합 객체를 모두 동일하게 다룰 수 있도록 하는 패턴
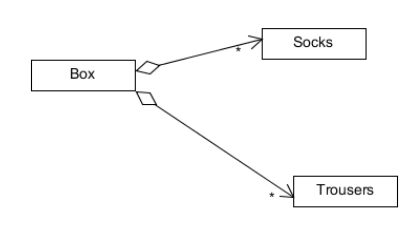
택배 박스안에 있는 물품들의 비용을 계산하는 예로 보자. 박스안에는 양말과 바지가 있다고 했을 때 클래스 구조는 다음과 같다.
Box
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class Box {
private List<Trousers> trousers = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Socks> socks = new ArrayList<>();
public int price() {
int tPrice = 0;
int sPrice = 0;
for (Trousers t : trousers) {
tPrice += t.price();
}
for (Socks s : socks) {
sPrice += s.price();
}
return tPrice + sPrice;
}
public void addSocks(Socks s) { socks.add(s); }
public void addTrousers(Trousers t) { trousers.add(t); }
}
Trousers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Trousers {
private int weight;
public Trousers(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int price() {
return this.weight/100*200;
}
}
Socks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Socks {
private int weight;
public Socks(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int price() {
return this.weight/100*200;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box box1 = new Box();
Socks s1 = new Socks(200);
Socks s2 = new Socks(300);
Trousers t1 = new Trousers(600);
box1.addSocks(s1);
box1.addSocks(s2);
box1.addTrousers(t1);
System.out.println(box1.price());
}
}
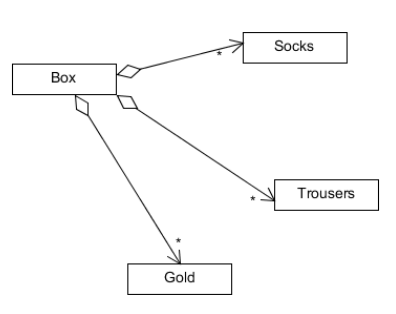
여기에서 박스에 만약 gold라는 아이템을 추가한다면 클래스 다이어그램은 다음과 같이 된다.
Gold
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Gold {
private int weight;
public Gold(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public int price() {
return this.weight/100*200;
}
}
수정 된 Box
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
public class Box {
private List<Trousers> trousers = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Socks> socks = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Gold> golds = new ArrayList<>();
public int price() {
int tPrice = 0;
int sPrice = 0;
for (Trousers t : trousers) {
tPrice += t.price();
}
for (Socks s : socks) {
sPrice += s.price();
}
for (Gold g : golds) {
gPrice += g.price();
}
return tPrice + sPrice + gPrice;
}
public void addSocks(Socks s) { socks.add(s); }
public void addTrousers(Trousers t) { trousers.add(t); }
public void addGolds(Gold g) { golds.add(g); }
}
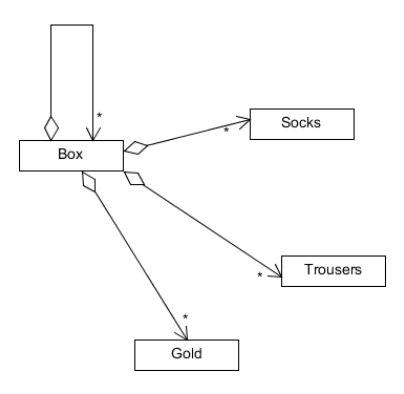
또한 박스안에 박스를 넣을 수 있기 때문에 박스 클래스는 자신과 집약관계를 맺을 수 있게 되고 클래스 다이어그램으로 나타내면 다음과 같다.
자신과 집약관계를 맺는 Box
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
public class Box {
private List<Trousers> trousers = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Socks> socks = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Gold> golds = new ArrayList<>();
private List<Box> boxes = new ArrayList<>();
public int price() {
int tPrice = 0;
int sPrice = 0;
int gPrice = 0;
int bPrice = 0;
for (Trousers t : trousers) {
tPrice += t.price();
}
for (Socks s : socks) {
sPrice += s.price();
}
for (Gold g : golds) {
gPrice += g.price();
}
for (Box b : boxes) {
bPrice += b.price();
}
return tPrice + sPrice + gPrice + bPrice;
}
public void addSocks(Socks s) { socks.add(s); }
public void addTrousers(Trousers t) { trousers.add(t); }
public void addGolds(Gold g) { golds.add(g); }
public void addBox(Box b) { boxes.add(b); }
}
클라이언트 코드 Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box box1 = new Box();
Socks s1 = new Socks(200);
Socks s2 = new Socks(300);
Trousers t1 = new Trousers(600);
box1.addSocks(s1);
box1.addSocks(s2);
box1.addTrousers(t1);
System.out.println(box1.price());
Box box2 = new Box();
Gold g1 = new Gold(800);
box2.addBox(box1);
box2.addGolds(g1);
System.out.println(box2.price());
}
}
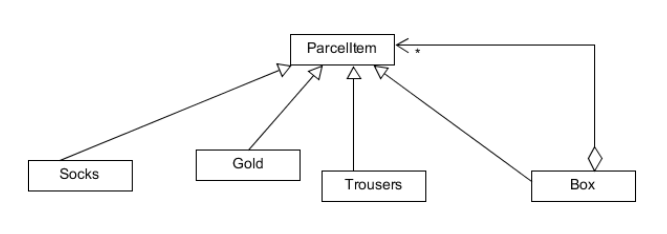
여기서 보면 벌써 새로운 아이템이 추가될 때마다 Box.java 클래스에서 새로운 아이템에 대한 가격 계산을 해야되므로 코드가 수정되어 OCP에 위배된다. 이럴때 사용하는 디자인 패턴이 컴포지트 패턴이고 택배에 넣을 수 있는 항목들을 포함하는 인터페이스 ParcelItem을 만들어 이를 상속하는 구조로 바꿔볼 수 있다.
ParcelItem을 상속하여 구성된 구조
ParcelItem
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public abstract class ParcelItem {
protected int weight;
public ParcelItem(int weight) {
this.weight = weight;
}
public abstract int price();
}
Trousers
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Trousers extends ParcelItem{
public Trousers(int weight) {
super(weight);
}
public int price() {
return this.weight/100*200;
}
}
Socks
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Socks extends ParcelItem{
public Socks(int weight) {
super(weight);
}
public int price() {
return weight/100*200;
}
}
Gold
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Gold extends ParcelItem{
public Gold(int weight) {
super(weight);
}
public int price() {
return this.weight/100*2000;
}
}
Box
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class Box extends ParcelItem{
private List<ParcelItem> items = new ArrayList<>();
public Box(int weight) {
super(weight);
}
public int price() {
int totalPrice = 0;
for (ParcelItem item : items) {
totalPrice += item.price();
}
return totalPrice;
}
public void addItems(ParcelItem item) { items.add(item); }
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Box box1 = new Box(0);
Socks s1 = new Socks(200);
Socks s2 = new Socks(300);
Trousers t1 = new Trousers(600);
box1.addItems(s1);
box1.addItems(s2);
box1.addItems(t1);
System.out.println(box1.price());
Box box2 = new Box(0);
Gold g1 = new Gold(800);
box2.addItems(box1);
box2.addItems(g1);
System.out.println(box2.price());
}
}
Composite 패턴은 전체-부분을 가지는 객체들 간의 관계를 정의할때 유용하다. 클라이언트는 전체와 부분을 구분하지 않고 동일한 인터페이스를 사용할 수 있다.
- Component : 구체적인 부분, 즉 Leaf 클래스와 전체에 해당하는 Composite 클래스에 공통 인터페이스를 정의함.
- Leaf : 구체적인 부분클래스로 Composite 객체의 부품으로 설정
- Composite : 전체 클래스로 복수 개의 Component를 갖도록 정의한다. 그러므로 복수 개의 Leaf, 심지어 복수 개의 Compostie 객체를 부분으로 가질 수 있다.