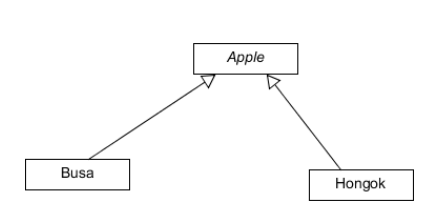
객체를 생성하기 위해 인터페이스를 정의하지만, 어떤 클래스의 인스턴스를 생성할지에 대한 결정은 서브클래스가 내리도록 하는 패턴
팩토리 메소드 패턴은 생성 패턴 중 하나로 이 패턴이 언제 적용 되는지 알기 위해 사과를 디저트로 제공하는 식당 클래스로 예를 들어보자
Apple
1
2
3
4
5
public abstract class Apple {
public abstract void wash();
public abstract void peel();
public abstract void slice();
}
Restaurant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Restaurant {
public Apple servingApple() {
Apple apple = new busa();
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
}
Busa
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Busa extends Apple {
@Override
public void wash() {
System.out.println("Busa: wash");
}
@Override
public void peel() {
System.out.println("Busa: peel");
}
@Override
public void slice() {
System.out.println("Busa: slice");
}
}
Hongok
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Hongok extends Apple {
@Override
public void wash() {
System.out.println("Hongok: wash");
}
@Override
public void peel() {
System.out.println("Hongok: peel");
}
@Override
public void slice() {
System.out.println("Hongok: slice");
}
}
만약 아침에 홍옥 사과를 먹는 클래스를 만들어보면 다음과 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
public class Home {
public Apple getAppleForBreakfast() {
Apple apple = new Hongok();
apple.wash();
return apple;
}
}
여기서 만약 사과의 종류가 변경된다고 해보자. 그럼 Restuarant 클래스와 Home 클래스에서 사과를 생성하는 명령어 부분을 다른 종류의 사과로 바꿔 생성자를 통해 생성 해야한다. 이렇게 되면 사과 인스턴스를 생성하는 모든 코드에서 계속해서 반복하여 작업하게 된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Restaurant {
public Apple servingApple(String kind) {
Apple apple = null;
if(kind.equals("busa")) apple = new Busa();
else if(kind.eqauls("hongok")) apple = new hongok();
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
}
이런식으로 kind 매개변수를 받고 kind에 따라 사과를 생성하는 방식으로 바꿀수 있지만 사과의 종류는 계속 변경되므로 이 부분을 따로 클래스로 분리하여 캡슐화한다. 이떄 사용하는 패턴이 팩토리 메소드 패턴으로 이 예제에서는 AppleFactory라는 클래스로 캡슐화를 하게 되면 아래의 코드와 같다.
AppleFactory
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class AppleFactory {
Apple apple = null;
if(kind.equals("busa")) apple = new Busa();
else if(kind.eqauls("hongok")) apple = new hongok();
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
Restuarant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class Restaurant {
public Apple servingApple(String kind) {
Apple apple = null;
Apple apple = factory.getApple(kind);
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
}
여기서 AppleFactory 메소드는 생성자를 생성하는 클래스이므로 여기에 싱글턴 패턴을 적용해서 코드를 다시 구성하게 된다면 아래와 같다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class AppleFactory {
private static AppleFactoryinstance= null;
private AppleFactory() {};
public static AppleFactory getInstance() {
if (instance== null)instance= new AppleFactory();
returninstance;
}
public Apple getApple(String kind) {
Apple apple = null;
if (kind.equals("busa")) apple = new Busa();
else if (kind.equals("hongok")) apple = new Hongok();
else if (kind.equals("hongro")) apple = new Hongro();
return apple;
}
}
Restaurant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class Restaurant {
public Apple servingApple(String kind) {
AppleFactory factory = AppleFactory.getInstance();
Apple apple = factory.getApple(kind);
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Restaurant r1 = new Restaurant();
r1.servingApple("busa");
}
}
- 팩토리 메소드 패턴은 객체를 생성하는 코드를 별도의 클래스/메소드로 분리함으로써 객체 생성 방식의 변화에 대비하는데 유용하다.
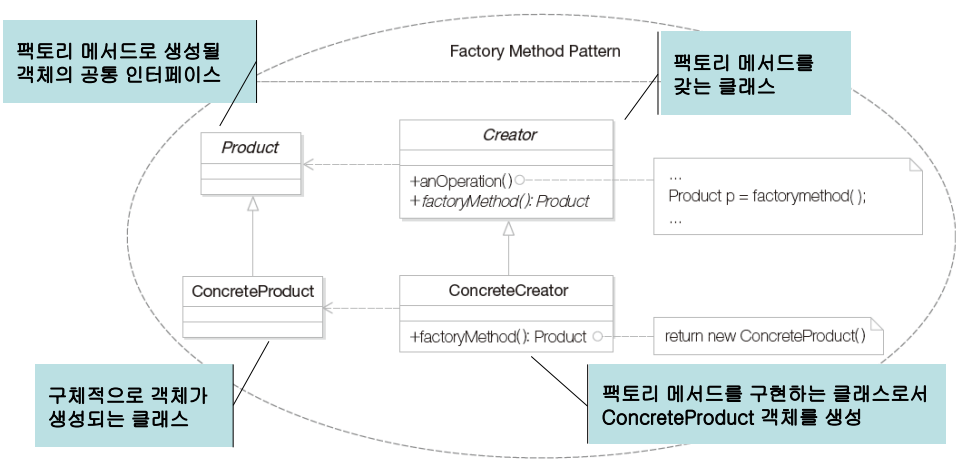
여기에 GoF의 팩토리 메소드 패턴을 소개하면 GoF의 팩토리 메소드 패턴은 템플릿 메소드 패턴을 이용하여 자식 클래스에서 생성자를 정의하도록 구성하였다.
Restuarant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public abstract class Restaurant {
public Apple servingApple(String kind) { //template method
Apple apple = getApple(kind); //factory method
apple.wash();
apple.peel();
apple.slice();
return apple;
}
public abstract Apple getApple(String kind);
}
전체적인 흐름에서 특정부분만 달라지기 때문에 사과를 얻어오는 지점만 Template Method을 적용할 수 있다.
여기서 servingApple 메소드는 전체적인 흐름을 기술하는 것이기 때문에 template method 이고 사과를 얻어오는 getApple은 각 지점마다 다르므로 하위 클래스에서 정의하는 factory method이다.
SeoulRestuarant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class SeoulRestaurant extends Restaurant {
@Override
public Apple getApple(String kind) {
Apple apple = null;
if (kind.equals("busa")) apple = new Busa();
if (kind.equals("hongok")) apple = new Hongok();
if (kind.equals("hongro")) apple = new Hongro();
return apple;
}
}
NYRestuarant
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
public class NYRestaurant extends Restaurant {
@Override
public Apple getApple(String kind) {
Apple apple = null;
if (kind.equals("koru"))apple = new Koru();
else if(kind.equals("crispy"))apple =new Everycrispy();
else if (kind.equals("pl"))apple =new Pinklady();
return apple;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Restaurant namgajwa = new SeoulRestaurant();
namgajwa.servingApple("busa");
Restaurant manha = new NYRestaurant();
manha.servingApple("pl");
}
}
- Product(Apple) : 팩토리 메소드로 생성될 객체의 공통 인터페이스
- ConcreteProduct(Busa, Hongok) : 구체적으로 객체가 생성되는 클래스
- Creator(Restuarant): 팩토리 메소드를 갖는 클래스
- ConcreteCreator(SeoulRestuarant) : 팩토리 메소드를 구현하는 클래스로 ConcreteProduct 객체를 생성한다.