싱글턴 패턴은 인스턴스가 오직 하나만 생성되는 것을 보장하고 어디에서든 이 인스턴스에 접근할 수 있도록 하는 디자인 패턴
1
2
3
4
5
싱글턴 패턴이 왜 쓰는지 알기 위해 예를 통해 살펴보자
ex) 공통 로그 파일에 모든 사용자 계좌의 입금/출금의 발생 내역을 기록
Account, Logger 클래스
Account
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class Account {
private String owner;
private int balance;
private Logger myLogger;
public Account(String owner, int balance) {
this.owner = owner;
this.balance = balance;
this.myLogger = new Logger();
}
public String getOwner() {
return owner;
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " + this.getOwner() + " deposit " + money);
balance += money;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " + this.getOwner() + " withdraw " + money);
balance -= money;
}
}
}
Account는 계좌를 생성하여 입금과 출금 기능을 제공한다.
Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
public Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void log(String message) {
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
}
Logger 클래스는 log.txt파일에 입금/출금 내역을 기록하는 일을 수행한다.
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acct1 = new Account("dong1", 1000000);
acct1.deposit(20000);
Account acct2 = new Account("dong2", 2000000);
acct2.withdraw(5000);
}
}
dong1과 dong2의 계좌를 생성하여 입금과 출금을 기록하는 일을 수행한다.
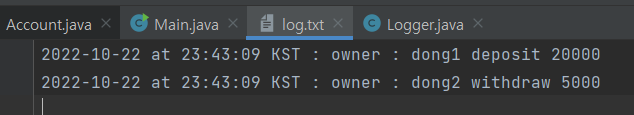
실행결과
1
→ dong1의 입금 내역이 누락되어 dong2의 출금내역만 log.txt에 출력된것을 볼 수 있다.
이는 하나의 인스턴스를 공유하는 것이 아닌 dong1과 dong2의 인스턴스를 각각 생성했기에 발생한 문제이다.
해결책
- 모든 Account 인스턴스가 하나의 Logger 인스턴스를 공유하도록 만들어야한다. 이를 위해 account 클래스를 수정하여 해결한다.
Account
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Account {
private String owner;
private int balance;
private Logger myLogger;
//Logger 인스턴스 생성 부분을 제거
public Account(String owner, int balance) {
this.owner = owner;
this.balance = balance;
}
public String getOwner() { return owner; }
public int getBalance() { return balance; }
public void deposit(int money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " +this.getOwner() + " deposit " + money);
balance += money;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " +this.getOwner() + " withdraw " + money);
balance -= money;
}
}
public void setMyLogger(Logger myLogger) {
this.myLogger = myLogger;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Logger logger = new Logger();
Account acct1 = new Account("insang1", 1000000);
acct1.setMyLogger(logger);
acct1.deposit(20000);
Account acct2 = new Account("insang2", 2000000);
acct2.setMyLogger(logger);
acct2.withdraw(5000);
}
}
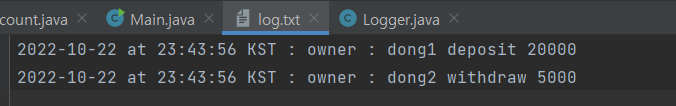
실행결과
but, 위와 같은 코드로 작성하게 되면 Logger 인스턴스를 외부에서 여러개 생성할 수 있게 된다. 따라서 외부에서 여러개 생성못하도록 막아야한다.
해결책
- 클래스가 하나의 인스턴스만을 가지도록 만드는 패턴을 싱글턴 패턴이라고 하며, 외부에서 생성자를 여러개 생성못하게 막고, 오직 하나의 인스턴스를 생성할 수 있게 해준다.
싱글턴 패턴
- static 변수 instance 선언
- 생성자를 private으로 선언
- Logger 인스턴스를 생성 및 반환하는 getInstance() 메소드 정의
Account
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
public class Account {
private String owner;
private int balance;
private Logger myLogger;
public Account(String owner, int balance) {
this.owner = owner;
this.balance = balance;
this.myLogger = Logger.getInstance();
}
public String getOwner() {
return owner;
}
public int getBalance() {
return balance;
}
public void deposit(int money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " + this.getOwner() + " deposit " + money);
balance += money;
}
public void withdraw(int money) {
if (balance >= money) {
myLogger.log("owner" + " : " + this.getOwner() + " withdraw " + money);
balance -= money;
}
}
}
Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
private static Logger instance;
public Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public void log(String message) {
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
public static Logger getInstance(){
if(instance== null)
instance= new Logger();
return instance;
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acct1 = new Account("dong1", 1000000);
acct1.deposit(20000);
Account acct2 = new Account("dong2", 2000000);
acct2.withdraw(5000);
}
}
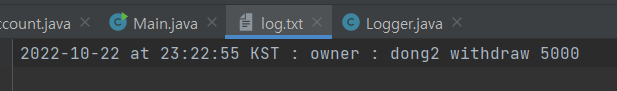
실행결과
→ 하나의 Logger 인스턴스를 공유해 문제없이 잘 수행된다.
다중스레드에서의 싱글턴 패턴
- 위의 예제에서 싱글턴 패턴을 적용하여 하나의 Logger 인스턴스를 생성하여 공유하도록 설계가 가능했지만 이는 다중스레드에서는 적용이 되지 않는다. 왜냐하면 각각의 스레드들이 여러개의 인스턴스를 생성하기 때문이다.
User
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class User extends Thread {
public User(String name) { super(name); }
public void run() {
Random r = new Random();
Account acct = new Account(Thread.currentThread().getName(), r.nextInt(1000000));
if (r.nextBoolean()) acct.withdraw(r.nextInt(acct.getBalance()));
else acct.deposit(r.nextInt(acct.getBalance()));
}
}
Main
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
User[] users = new User[10];
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
users[i] = new User("dong"+i);
users[i].start();
}
}
}
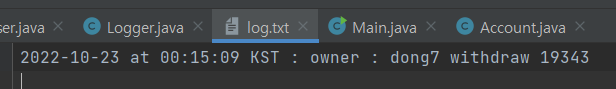
실행결과
→ 위의 실행결과와 같이 다중스레드 환경에서는 하나의 내역만 출력되고 인스턴스는 여러개가 생성된것을 알 수 있다.
해결책
- Synchronized
- DCL(Double Checked Locking)
- Initialization on demand holder idiom
1. Synchronized
→ synchronized를 이용해 race condition이 발생하지 않게 만든다.
Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
private static Loggerinstance;
private Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
//Logger 메서드에 synchronized 추가
public synchronized static Logger getInstance() {
if (instance== null)
instance= new Logger();
return instance;
}
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println(this.toString());
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
}
syncrhonized로 해결 가능하지만 synchronized 사용 시 내부적으로 많은 cost가 발생하고 많은 thread 들이 getInstance()를 호출하게 되면 프로그램 전반적인 성능저하가 발생
2. DCL(Double Checked Locking)
→ synchronized의 비효율성을 해결하기 위해 dcl기법을 적용해 instance가 생성되었는지를 두번 체크하는 로직이다.
Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
private volatile static Loggerinstance;
private Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {
}
}
public static Logger getInstance() {
if (instance== null) {
synchronized (Logger.class) {
if (instance== null) {
instance= new Logger();
}
}
}
return instance;
}
public void log(String message) {
System.out.println(this.toString());
SimpleDateFormat formatter = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
}
dcl 기법으로 보완은 가능하지만 명령어 reorder가 발생할 수 있어 미완성 인스턴스가 다른 스레드에게서 생성 될 수 있다.
3. Initialization on demand holder idiom
→ 앞서 dcl 기법과 synchronzied 기법을 안쓰고 동시성 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
Logger
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
public Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
public void log (String message) {
System.out.println(this.toString());
SimpleDateFormat formatter= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
private static class LazyHolder {
public static final LoggerINSTANCE= new Logger();
}
public static Logger getInstance() {
return LazyHolder.INSTANCE;
}
}
현재까지 가장 많이 사용되는 방법이며 Singleton 클래스에는 LazyHolder 클래스의 변수가 없기 때문에 Singleton 클래스 로딩 시 LazyHolder 클래스를 초기화하지 않는다.
또한 Class를 로딩하고 초기화하는 시점은 thread-safe를 보장하고 holder 안에 선언된 instance가 static이기 때문에 클래스 로딩 시점에 한번만 호출
→final을 써서 다시 값이 할당되지 않도록 함
정적 클래스를 이용하여 싱글턴 패턴을 이용할 수 있지만 가장 차이나는 점은 정적 클래스를 이용하면 객체를 전혀 생성하지 않고 메서드를 사용한다는 점이다 → but, 인터페이스의 경우 정적 메서드는 사용 불가하기 때문에 사용할 수 없는 경우가 있다.
싱글턴 생성 방식 2가지
1. Eager initialization
2. Lazy initialization
Eager initialization
→ 싱글톤 객체를 미리 생성하는 기본적인 Singleton 방식
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
private static Loggerinstance= new Logger();
private Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
public static Logger getInstance() { returninstance; }
public void log (String message) {
SimpleDateFormat formatter= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
}
클래스 로딩 시점에 초기화되어 인스턴스가 필요하지 않는 경우에도 생성
→ 따라서 인스턴스가 필요할 떄 생성하는 lazy initialization을 써야한다.
Lazy initialization
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
public class Logger {
private final String LOGFILE = "log.txt";
private PrintWriter writer;
private static Loggerinstance;
private Logger() {
try {
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(LOGFILE);
writer = new PrintWriter(fw, true);
} catch (IOException e) {}
}
public static Logger getInstance() {
if (instance== null)instance= new Logger();
returninstance;
}
public void log (String message) {
SimpleDateFormat formatter= new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z");
Date date = new Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
writer.println(formatter.format(date) + " : " + message);
}
}